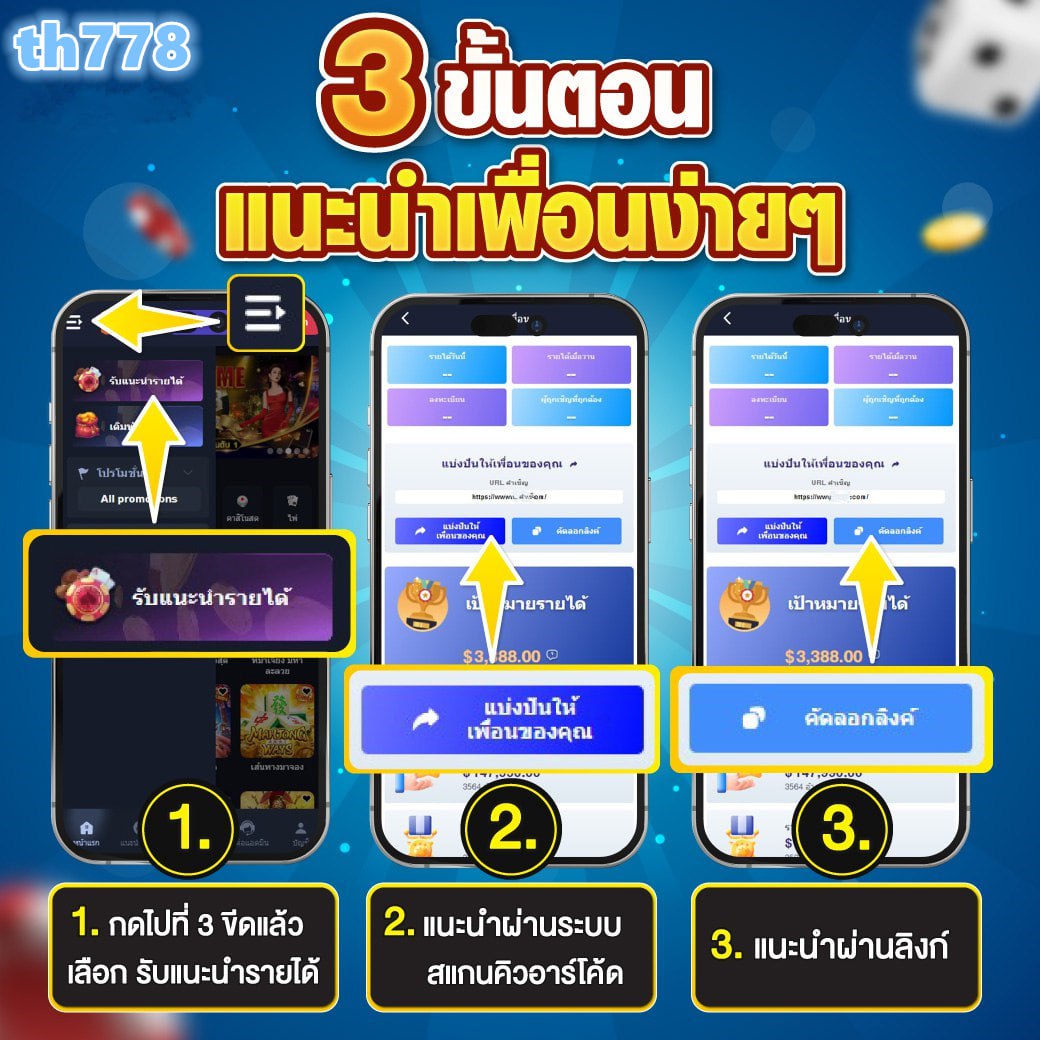
สุกี้สล็อต
฿10.00
สุกี้สล็อต สุกี้สล็อต https: · หน้าหลัก · สมัครสมาชิก · วิธีการใช้งาน · ติดต่อเรา.
สุกี้สล็อต555 ... ทางเข้า :https:?token=QiJpE3r5gZ9XnOz8… ขอคนละ ➡️ 1 ... #อเวจี เครดิตฟรี 100฿. สมาชิกใหม่ เก่า โค้ดฟรี DDUF-9UMH-D322 ♻️ ฝากกดรี + ติดตาม + เม้น #นักปั่น ...
สุกี้สล็อต ภาพรวมธุรกิจ. ออกแบบและผลิตเสาโทรคมนาคม · ออกแบบผลิตเสาส่งไฟฟ้าแรงสูง และสถานีไฟฟ้าย่อย · งานโครงสร้างโลหะ · การชุบเคลือบสังกะสี · สินค้าอุตสาหกรรม · นักลงทุนสัมพันธ์ · ข้อมูลบริษัท; ข้อมูล ...
สุกี้สล็อต555 pg slot เรามีเกมคาสิโนและกีฬาในที่เดียว เลือกเล่นได้ตามสไตล์คุณ พร้อมสะสมแต้มไปแลกรางวัลในอนาคตด้วย หรือจะเป็นสายหมุนวงล้อ หรือสายกีฬา ที่นี่มีให้ครบ ไม่ต้องโหลดแอป!
Add to wish list- SKU:681066576
- Category:Game
- Tags:สุกี้สล็อต
Product description
สุกี้สล็อตสุกี้สล็อต ✅ Play 17,500+ Free Slot Games 98.5% RTP No Download สุกี้สล็อต,https: · หน้าหลัก · สมัครสมาชิก · วิธีการใช้งาน · ติดต่อเรา.&emspจริงเหรอ?? . Marvel Studios' The Fantastic Four: First Steps 24 กรกฎาคมนี้ 🕶️ IMAX 3D เสียงต้นฉบับซับไทย: ทุกสาขา IMAX ...