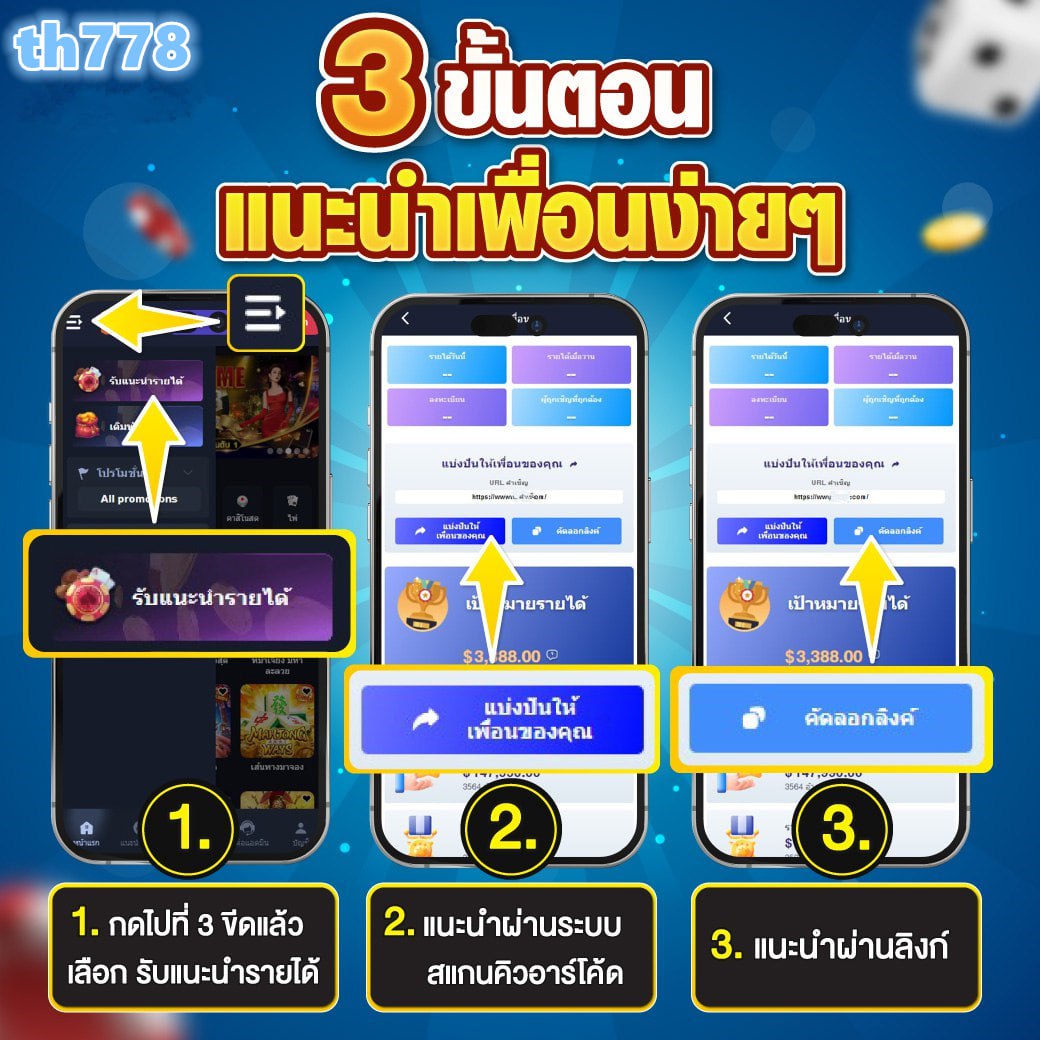
เรมันนี่สล็อต
฿10.00
เรมันนี่สล็อต เรมันนี่สล็อต99 เรมันนี่สล็อต เกมสล็อตเว็บตรง รับเคล็ดลับเกี่ยวกับวิธีการเล่นสล็อตคาสิโนออนไลน์เพื่อความบันเทิงและกำไรของคุณกับ เรมันนี่สล็อต พร้อมเทคนิคการเล่นที่จะช่วยให้คุณชนะ
เรมันนี่สล็อต เรมันนี่สล็อต เกมสล็อตเว็บตรง รับเคล็ดลับเกี่ยวกับวิธีการเล่นสล็อตคาสิโนออนไลน์เพื่อความบันเทิงและกำไรของคุณกับ เรมันนี่สล็อต พร้อมเทคนิคการเล่นที่จะช่วยให้คุณชนะ
เรมันนี่สล็อตดาวน์โหลด เรมันนี่สล็อต เกมสล็อตเว็บตรง รับเคล็ดลับเกี่ยวกับวิธีการเล่นสล็อตคาสิโนออนไลน์เพื่อความบันเทิงและกำไรของคุณกับ เรมันนี่สล็อต พร้อมเทคนิคการเล่นที่จะช่วยให้คุณชนะ
เรมันนี่สล็อต apk เรมันนี่สล็อต เกมสล็อตเว็บตรง รับเคล็ดลับเกี่ยวกับวิธีการเล่นสล็อตคาสิโนออนไลน์เพื่อความบันเทิงและกำไรของคุณกับ เรมันนี่สล็อต พร้อมเทคนิคการเล่นที่จะช่วยให้คุณชนะ
Add to wish list- SKU:673144284
- Category:Game
- Tags:เรมันนี่สล็อต
Product description
เรมันนี่สล็อตเรมันนี่สล็อต ✅ เรมันนี่สล็อต เกมสล็อตเว็บตรง เว็บไซต์สดและเคล็ดลับการเดิมพัน 1 2025 เรมันนี่สล็อต,เรมันนี่สล็อต เกมสล็อตเว็บตรง รับเคล็ดลับเกี่ยวกับวิธีการเล่นสล็อตคาสิโนออนไลน์เพื่อความบันเทิงและกำไรของคุณกับ เรมันนี่สล็อต พร้อมเทคนิคการเล่นที่จะช่วยให้คุณชนะ &emspเรมันนี่สล็อต เกมสล็อตเว็บตรง รับเคล็ดลับเกี่ยวกับวิธีการเล่นสล็อตคาสิโนออนไลน์เพื่อความบันเทิงและกำไรของคุณกับ เรมันนี่สล็อต พร้อมเทคนิคการเล่นที่จะช่วยให้คุณชนะ