hydra 24h สล็อต
฿10.00
hydra 24h สล็อต เว็บสล็อตทุนน้อย ฝาก10รับ100 HYDRA24H แตกง่าย จ่ายดี ยูสใหม่แตกโครตง่าย สมัครสมาชิกฟรี ฝาก-ถอน คาสิโนออนไลน์ชั้นนำ อันดับ 1 ของประเทศ ทีมงานบริการตลอด 24 ชม
4×4 สล็อตเว็บตรงสีแดง HYDRA24H แตกง่าย จ่ายดี ยูสใหม่แตกโครตง่าย สมัครสมาชิกฟรี ฝาก-ถอน คาสิโนออนไลน์ชั้นนำ อันดับ 1 ของประเทศ ทีมงานบริการตลอด 24 ชม
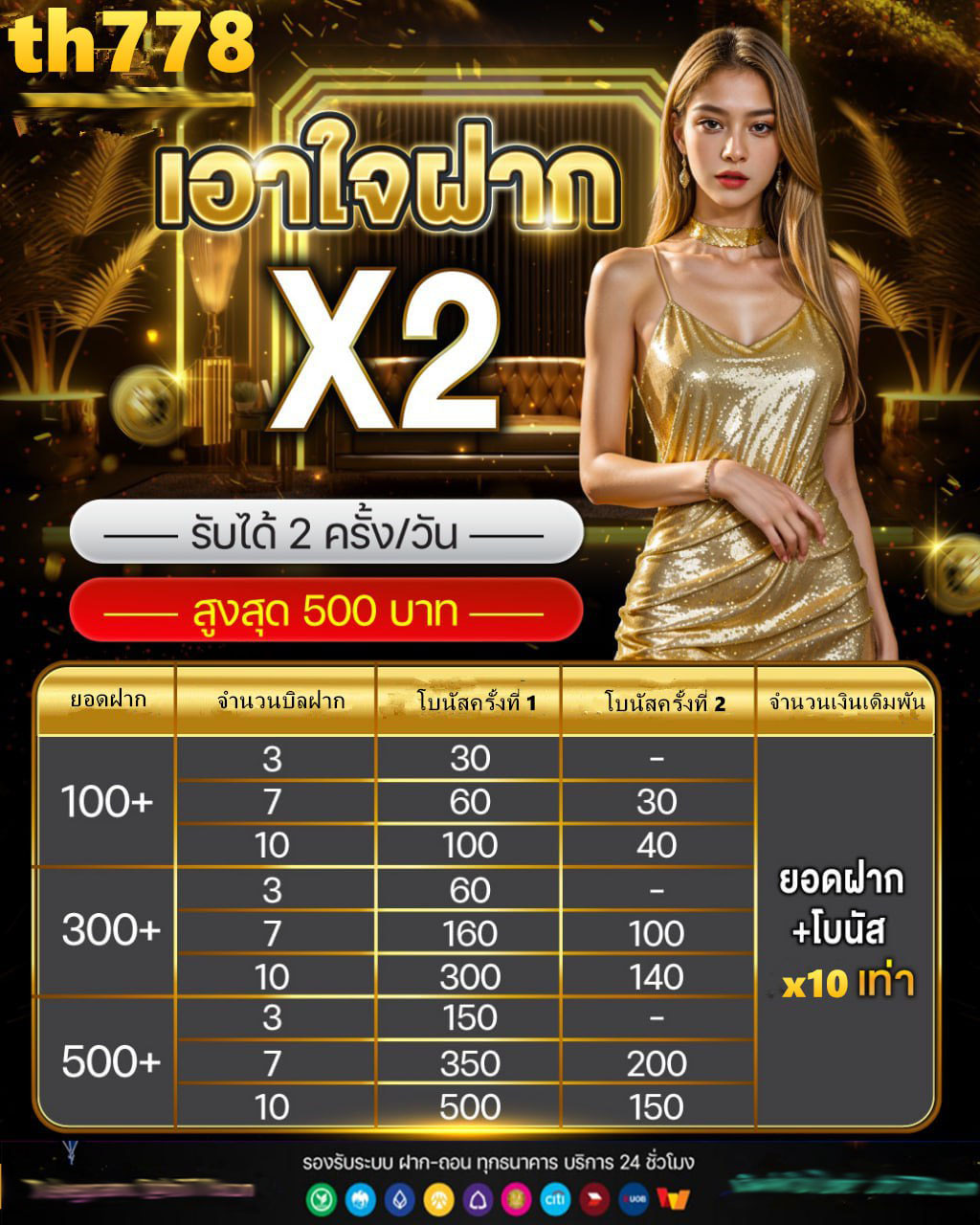
เว็บ ผึ้ง สล็อต HYDRA24H บิลใหญ่ บิลเล็ก เราก็แจกยับ โปรดุเดือดประจำเดือน ฝากเพียง 20 รับเลย 100 ที่นี่ : hydra-24h #สล็อตเกมส์ #สล็อตฟรีเครดิต #pgslot #ฝาก1รับ100ล่าสุด #ฝาก10
สล็อต 168 เว็บตรง วอ เลท #hydra24h ล่าสมบัติ แจกโค้ดเครดิตฟรี 50 บาท ▪️ไม่ต้องฝากก่อน ▪️รับได้ทุกยูสเซอร์ ▪️ ทำยอดเทิร์นเพียงแค่ 300 ถอนไม่อั้น รับเครดิต : eE2B7bm No photo description
Add to wish list- SKU:630560283
- Category:Game
- Tags:hydra 24h สล็อต
Product description
hydra 24h สล็อตhydra 24h สล็อต ✅ สล็อต24h - คาสิโนสล็อตยอดนิยม เล่นง่าย 24 ชั่วโมง hydra 24h สล็อต,HYDRA24H แตกง่าย จ่ายดี ยูสใหม่แตกโครตง่าย สมัครสมาชิกฟรี ฝาก-ถอน คาสิโนออนไลน์ชั้นนำ อันดับ 1 ของประเทศ ทีมงานบริการตลอด 24 ชม &emsphydra24h แพลตฟอร์มพนันออนไลน์ที่ดีที่สุด slot bet เล่นง่าย สมัครเข้าสู่ระบบรับโปรโมชั่นโบนัสสุดพิเศษมากมาย สัมผัสความตื่นเต้นที่ทางเข้าเล่นเกมพนันที่คุณรัก